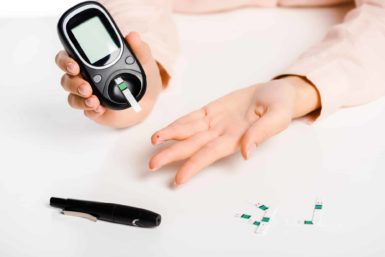
The diabetic test strip is one of three main components needed to test your blood sugar levels at home. The other two are the blood glucose monitor and the lancing device. When used together, you will receive a very accurate reading of your blood sugar level that is typically displayed in mg/dL, which stands for milligrams per deciliter.
A healthy person will have anywhere between 70 to 100 mg/dL of blood sugar when fasting. That number can go as high as 180 shortly after a meal. A person with diabetes can experience numbers anywhere between 130 and 300 on average when fasting depending on how well they maintain their condition. Of course, a well-maintained diabetic patient can enjoy a life with blood sugar levels between 70 and 100 mg/dL as well.
The point of the diabetic test strip is to let you know exactly where you stand on this scale. If your blood sugar is too high, then you may need to take insulin shot if you are prescribed them. At the very least, you will know that something in your routine is not right. That may require changing your medication or you’re eating habits.
Most diabetic patients are advised to test their blood sugar around four times a day. However, your doctor may advise a different frequency and you should always take their advice. Many patients have forgotten how to use their diabetic test strips or may have never been properly taught in the first place. We’re your #1 Diabetic Test Strip Buyers. Get best deals on cash for your diabetic test strips At More Cash for Test Strips. Our Business hours are 9:30 to 6:30 Pacific Time Monday to Friday have questions call or text 310-892-2808.
How To Use Diabetic Test Strips At Home
Using your diabetic test strips is actually a very simple process. The first step is to wash and dry your hands with warm water. This reduces the likelihood of any interference and it helps increase blood flow in the area. Next, you will need to follow the instructions for your glucose meter to turn it on and prepare for a sample. Most glucose monitors will turn on automatically when a diabetic test strip is inserted. Ensure that the monitor is powered on and the test strip is facing in the correct direction.
Now comes everyone’s least favorite part. You will need to take a lancing device and prick a small hole on your finger. You’re advised to find slightly different spots each time to reduce the pain. Many people prefer to use the side of their fingertip where it is slightly less sensitive. Once a drop of blood appears at the spot you are ready to use the device.
Take the glucose meter with the test strip inserted and hold it so that the exposed end of the strip is near the drop of blood. Upon contact, the strip should absorb the blood and the meter will begin to test the sample. Your blood glucose levels should be displayed within moments. It’s also a good idea to record your reading in a logbook.
Some specifics of this process may vary according to your brand of glucose meter and diabetic test strips. These devices tend to work the same only some come with additional features. For example, some glucose monitors include a digital logbook that automatically records information about your reading.
The Science Of A Test Strip
Now that you know to use diabetic test strips let’s take a quick look at how these strips actually work. The science is relatively the same for most diabetic test strips despite a large difference in price from one brand to the next. The average test strip is designed with several different layers and each layer serves a very specific purpose.
The top layer of the strip is responsible for absorbing the blood sample. It is designed like a sponge that runs a short distance from the tip of the strip. A more expensive test strip will have a higher quality material here. This makes it more likely to properly absorb the sample on the first attempt, thus reducing the need for multiple pricks.
The middle of the strip contains multiple layers that filter the blood sample and allow it to move to the appropriate areas near the bottom. Below these filters are layers that contain certain chemicals. One layer contains an enzyme that reacts with the blood sample. Another layer contains a chemical that accelerates the movement of electrons. A third layer contains stabilizing chemicals that help with both of the above processes.
The final layer contains the circuitry components of the strip. This is typically a thin circuit made from gold. It is responsible for transferring the electrons created in the chemical reaction to the glucose monitor. The use of gold allows the electrons to move as quickly as possible.
Why test blood sugar?
Testing for blood sugar provides important information for managing diabetes. It may help you in:
- Monitor how diabetes medicines affect your blood sugar levels.
- Consult your treatment team for advice on adjusting the dosage of diabetes medicine.
- Determine if your blood sugar is high or low. Then, adjust your treatment to address high blood sugar or take highly effective carbohydrates if you have low blood sugar.
- Track your progress toward your treatment goals.
- Find out how blood sugar is impacted by diet and exercise.
- Know how other factors, including sickness or stress, might impact blood sugar levels.
When to test blood sugar
A doctor can tell you how often to monitor blood sugar levels—the type of diabetes you have and the treatment plan will usually determine the answer.
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor can recommend a CGM or blood sugar test four to ten times a day. It might be necessary to test:
- Before snacks and meals and occasionally after meals.
- Before, during, and occasionally after exercise.
- Before bed.
- Sometimes at night.
- After low blood sugar treatment.
- More often when you’re sick.
- More often if you alter your daily routine.
- More often when taking a new medicine.
Type 2 diabetes
The medical professional may recommend continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) if you use insulin for type 2 diabetes. Alternatively, many daily blood sugar tests can be necessary. The kind and quantity of insulin you use will determine how often you need to do this. Testing is frequently recommended before meals and bed if you take a couple of insulin injections daily. Should you use an intermediate- or long-acting insulin, you might only need to test before breakfast and occasionally before dinner or bed.
Generally speaking, you may need more frequent testing if you:
- Are sick.
- Have to make a long drive.
- Change the way you exercise or eat.
If you take medication other than insulin to control your type 2 diabetes, you may not have to test your blood sugar daily. Additionally, if you control the condition with exercise and diet alone, you may not have to test daily.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)
Individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, may decide to utilize CGMs. Every few minutes, CGMs take a blood sugar reading. They employ a sensor positioned beneath the skin and a device applied to it. It takes two weeks and ten days for these single-use sensors to be replaced. The lifespan of other implanted sensor types is up to six months.
A transmitter, a wireless device put on the body, is a component of CGMs. A program that displays the blood sugar level receives data from the sensor via the transmitter. An insulin pump, a smartphone, or a receiver can all display the application.
Certain CGMs display your blood sugar level continuously. Frequently, they come with an alert that sounds if the blood sugar levels rise or fall too quickly. With other CGMs, you must run the receiver through the sensor to monitor your blood sugar. This might need to be done every few hours, but it is a more frequent task for some people.
Certain CGMs still require finger-stick blood testing. These tests set CGM. We refer to this as calibrating. The finger-stick blood tests also contribute to the accuracy of the CGM results. See the user manual for your equipment to determine if finger-stick blood tests are necessary and, if so, how frequently.
Wine may distort some CGM readings. Certain medications may affect the readings, particularly when taken with older CGMs. Among the medications that could influence blood sugar measurements are:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
- Aspirin.
- Albuterol (Ventolin HFA, Proair HFA, others).
- Atenolol (Tenormin, Tenoretic).
- Ethanol oleate (Ethamolin).
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor, Atorvaliq).
- Lisinopril (Qbrelis, Zestril).
- Vitamin C supplements (such as Airborne, Emergen-C, and others) are also sold.
Newer CGM readings appear unaffected by typical acetaminophen doses, which can reach 1,000 mg for an adult. Supplements containing fewer than 500 milligrams of ascorbic acid also don’t seem to impact more recent CGM readings.
Consult the packaging information that comes with the sensor if you must take any medication that can impair the accuracy of the readings. Alternatively, consult a medical professional. You can be instructed to use a regular blood sugar meter to confirm the results of your CGM once more. See your doctor about using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) if you are:
- Pregnant.
- Very ill.
- On dialysis.
These conditions could have an impact on a CGM’s blood sugar readings.
Know your target range
Find out from the doctors what your ideal blood sugar range is. Together, you and your doctor will determine your goal blood-sugar test results depending on several factors, such as:
- The type of diabetes that you have.
- Your age.
- Symptoms
- How long have you had diabetes.
- Whether you are pregnant or not.
- Any diabetes-related health conditions you may have.
- Your overall condition and any other medical problems you may have.
- The cost, intricacy, and frequency of side effects on diabetes medications.
The target blood sugar levels shown below are generally advised by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). These targets apply to most healthy individuals with diabetes who use medicine:
- Before meals, take 80 and 130 (mg/dL), or 4.4-7.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
- Less than 180 milligrams per deciliter (10.0 mmol/L) for two hours after meals.
However, according to the ADA, these goals frequently vary. Your age and health will determine your goals. Let the doctor know if your blood sugar is frequently outside your desired range.
Certain individuals will aim for slightly higher blood sugar levels, such as those who:
- Are sixty years of age or older.
- Have other medical issues, like lung, heart, or kidney disease.
- Feel no signs of hypoglycemia. We refer to this as low in sugar unawareness.
Instructions for Checking Your Blood Sugar
Your healthcare provider will advise you on how frequently to monitor your blood sugar. Additionally, they will advise you on the ideal blood sugar level. Your blood sugar target range is this. Your current treatment plan and general health will determine your blood sugar target range.
When you’re prepared to begin, quickly wash with water and soap. Make sure they are completely dry. Wet hands can harm blood glucose test strips or reduce the accuracy of your results.
Gather your supplies
Arrange your supplies on a clean surface. Putting them according to how you want to use them is helpful. What you’ll need is:
- A new lancet.
- Lancing device.
- Your blood glucose meter.
- An alcohol pad (in case you cannot wash your hands in a sink).
- A gauze pad or dry tissue (if you don’t have access to a sink to clean your hands).
- A trash container.
- Your blood glucose log.
- A sturdy container, like a hefty plastic laundry detergent bottle with a lid, to dispose of the used lancet.
When you remove a blood glucose test strip from its container, place it on the top of your meter. That makes it easy to pick up and keeps it dry and clean. Make sure the container holding the glucose test strips is closed tightly. Air humidity has the potential to harm the strips.
Prepare your lancing device
- To unlock the endcap, twist your lancing device’s white band to the right.
- Grasp the lancet by its circular tab. Push it firmly into the center of the lancing device till it is completely stuck.
- Twist the circular tab three times with care. Take care to avoid bending it. Remove the tab and store it for later use. There should be a tiny needle visible in the tab’s place.
- Put the endcap in an unlocked position on your lancing device.
- To adjust the puncture depth, turn the endcap dial’s black section. It is recommended to start with level 1 or 2. If the blood drop is not large enough, you can adjust it to a greater level.
Your lancing tool is now ready. Place it down. Take out your test strip and blood glucose meter.
Prepare your blood glucose meter
- Hold the test strip so that the printed side faces you.
- Hold the blood glucose meter with the buttons and screen facing you.
- Put the test strip’s grey square end on your meter’s test strip port.
Once the test strip is inserted into the port, your meter should activate and begin to beep. If not, then:
- Check that the test strip is fully inserted into the port.
- Check that the test strip’s grey square-adorned end is inserted into the port.
- Ensure that the test strip’s printed side is facing you.
Your glucose meter is now ready. The test strip will remain on for three minutes after you insert it. If you do not add a drop of blood to the tip within that period, the test strip will beep and turn off. If this occurs, remove the test strip and replace it in the port.
Avoid putting blood on the test strip when the meter goes off or before inserting it. Doing so could ruin the strip, and you’ll need to start with a new one.
Prick your finger
- Choose the finger that will be punctured. The side of the fingertip is what we advise using. Your fingertip’s middle and tip become more sensitive.
- Use a different spot every time. It helps prevent sore spots. Keep in mind that each fingertip can be used on both sides.
- Use the alcohol pad to clean the area if you still need to clean your hands. Dry it using a fresh tissue or gauze pad.
- Press the release button while maintaining a firm grip on the side of the finger with the lancing device. Then immediately remove the lancing tool from your finger. Look for a drop of blood.
- You might have to give your finger a light massage or squeeze. Don’t push yourself too hard on this. Your results might not be correct if you do.
- If the blood drop is too tiny, it may need to be pricked again. Using the same lancet is okay.
- Pull the white reset handle from the lancing device until it clicks into place.
- Turn the endcap dial to raise the puncture depth to a single level.
- Ensure that the lancing device is securely positioned against the side of the finger.
- Press the release button. Then immediately remove the lancing equipment from your finger.
- Look for a drop of blood. You should give your finger a gentle massage.
- If the blood drop is larger than required, reduce the puncture depth by one the next time you use your lancing equipment. It will prevent the lancet from prickling your finger as deeply.
Touch your blood glucose strips with the blood drop
- Once the blood drop is large enough, touch the test strip’s tip to the drop. The test strip will be filled with blood, whether on the side, bottom, or top of the strip.
- If insufficient blood is detected during the first attempt, your meter will beep twice, and a blood drop will appear on the display. Within 60 seconds, you can reapply more blood to the test strip.
- Your meter will display an error code if you don’t administer enough blood in 60 seconds. If this happens, remove the test strip and discard it. Take a fresh test strip and start over. If necessary, raise the lancing device’s piercing depth.
- When the test strip has received sufficient blood, your meter will start to beep and count down from five. Your blood sugar level will be displayed on the screen, with a color indicator next to the test strip port. It is referred to as the smartLIGHT or Target Light. If the result is within the intended range, you’ll see green; if it’s too high, you’ll see yellow; if it’s too low, you’ll see red.
- When you first obtain your Contour Next One blood sugar meter, the target glucose range is 70 to 180 mg/dL.
- You can use the Contour Diabetes app to adjust your goal range if your diabetes provider offers a different one.
- Using a Contour Diabetes app, you can disable the smartLIGHT feature if you would instead not use it.
Paying attention to the screen’s number and color is crucial.
Write your blood sugar level
- In a blood sugar journal, write your current blood sugar level. Your result will remain visible on the screen until you remove the test strip or after three minutes.
- When reading your blood glucose meter, ensure it is facing correctly. Also, ensure you can read the date and time just to be sure.
Get rid of the test strip and lancet
- Remove the test strip from the blood glucose meter firmly. Then, put it in the garbage and discard it- you can dispose of it with your normal trash.
- To unlock the endcap, rotate the white band on the lancing device to the right. Pull the endcap off straight.
- Place the round plastic tab you extracted from the lancet’s top on a level surface. Firmly insert the lancet’s tip into the plastic tab. The tab will cover the lancet to prevent unintentional self-pricking.
- Place the lancet over a sharp container made of plastic. Slide the lancet ejector forward till the lancet lands in the plastic sharps container.
- Don’t use your fingers to remove the lancet. The plastic tab is simple to remove. If it does, the needle might prick you.
- Replacing the lancet ejector requires sliding. Reinstall the endcap on your lancing apparatus. To lock on the endcap, twist the white band on the left.
Glucose Monitoring in Children
Children with any kind of diabetes should also monitor their glucose levels. Children may require more frequent testing than adults, mainly if they are insulin users.
Conducting regular glucose testing of your child can benefit them in the following ways:
- Solving problems with the treatment plan
- Giving them a sense of control over the situation
- Their comprehension of the effects of diet, exercise, and medicine on blood sugar
Moreover, children’s glucose goal ranges may be higher than adults. Their healthcare professional can determine a child’s optimal range.
It can be necessary to do nighttime blood sugar testing on kids who experience hypoglycemia or low blood sugar episodes.
In addition, more testing can be necessary if your child is ill.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions.
Can I reuse diabetic test strips?
No, it’s crucial not to reuse test strips as they are designed for single use. Reusing them can lead to inaccurate readings and compromise the effectiveness of monitoring your blood glucose levels. After using your used glucose meters, properly dispose of them in a garbage container.
Can diabetic test strips be used for diagnosing diabetes or only for monitoring?
Diabetic test strips are primarily used to monitor blood glucose levels rather than diagnose diabetes, usually diagnosed through specific blood tests conducted by healthcare professionals.
Do I need to cap the blood drop on the test strip and why is it important?
Yes, capping the blood drop on the test strip is crucial. It helps ensure an accurate reading by preventing contamination and maintaining the integrity of the blood sample.
Can I use diabetic test strips during pregnancy for gestational diabetes monitoring?
Yes, diabetic test strips can be used during pregnancy to monitor blood glucose levels for gestational diabetes. Consult your healthcare provider for specific guidance and monitoring frequency tailored to your pregnancy.
How can I ensure the proper disposal of used lancets and test strips?
Place used lancets in a puncture-resistant container and dispose of them according to local regulations. Used test strips can be disposed of in regular household trash but should be sealed safely to prevent accidental injury.
Making Use Of Your Strips
Don’t let your test strips go to waste. Some people don’t know how to use diabetic test strips and they sit in their medicine cabinet for years. We buy diabetic test strips so you don’t have to let them go to waste. Click here for more information on how to get rid of your unwanted testing strips. Or if you have a question simply send us an email here and we will get right back to you. Those people have an increased risk for complications. Now you know how to use the strips and the science of how they work. Please, test your blood sugar as recommended by your doctor and do everything necessary to control the numbers. More Cash For Test Strips offer cash for diabetic supplies. We buy diabetic test strips, get an instant quote, send them to us and get paid!

